- Praktijk-/online-afspraakverdeling
- Vasculaire compressiesyndromen
- Heeft u vragen?
- Checklist vasculaire compressie syndromen
- Musculoskeletale kenmerken van de vrouwelijke puberteit
- Lordosis /Swayback- Oorsprong van vele abdominale compressie syndromen
- Notenkraker-Syndroom is een verkeerde benaming! Lordogenetische linker nieradercompressie is een meer toepasselijke naam!
- May-Thurner-constellatie (May-Thurner-syndroom, Cockett’s syndroom)
- Middellijn (congestie) syndroom
- Bekkenverstoppingssyndroom
- Coeliakie Strandcompressie / Dunbar-syndroom / MALS / Arcuate ligament-syndroom
- Wilkie-Syndroom / Superieur-mescentraal-kwartiersyndroom
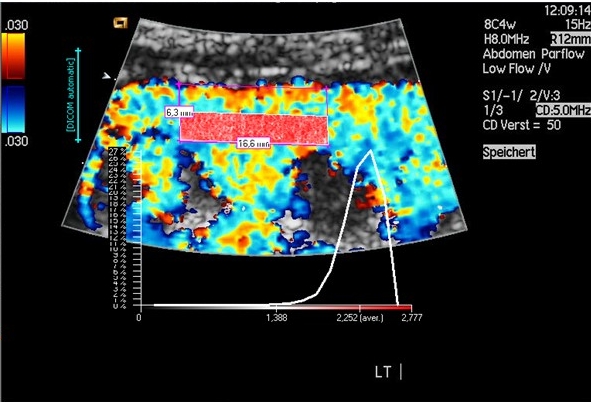
- Evlauatie van vasculaire compressies met de PixelFlux-methode
- Pudendale neuralgie bij vasculaire compressiesyndromen
- Migraine en multiple sclerose
- Behandeling van vasculaire compressiesyndromen
- Recent ontdekte vasculaire compressiesyndromen
- Echografie Diagnostiek
- Dienstenpakket
- Functionele kleur Doppler ultrasound – hoe ik het doe
- Perfusiemeting – PixelFlux-methode
- Onderzoek
- Publicaties
- Documenten geschreven door Th. Scholbach
- Eigen publicaties
- Inauguratie van metingen van de weefselpulsatiliteitsindex bij niertransplantaties
- Van notenkraker fenomeen tot middellijn congestie syndroom en de behandeling met aspirine
- Eerste sonografische weefselperfusie meting bij niertransplantaties
- Eerste sonografische tumor perfusie meting en correlatie met tumor oxygenatie
- Eerste sonographische darmwandperfusiemeting bij de ziekte van Crohn
- Eerste sonografische nierweefsel perfuisonmeting
- Eerste sonografische meting van nierperfusieverlies bij diabetes mellitus
- PixelFlux metingen van nierweefsel perfusie
- Publicaties
- Expertise
- Infectie met het Bornavirus
- Wetenschappelijke samenwerking
- Cookiebeleid
- Opmerkingen over medische verklaringen
- Gegevensbescherming
- Cookie Policy (EU)

Inflammation Diagnostics
Inflammation increases the perfusion of the affected organs and tissues. Body is reacting on the inflammaiton by widening the blood vessels in order to transport more immune cells to the location of the inflammation.
Crohn Disease
Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn Disease and Ulcerative Colitis come in phases. Here the measurement of bowel wall perfusion in Crohn Disease is demonstrated: red column – healthy colon; green column – actively inflamed part of the same intestinal segment.
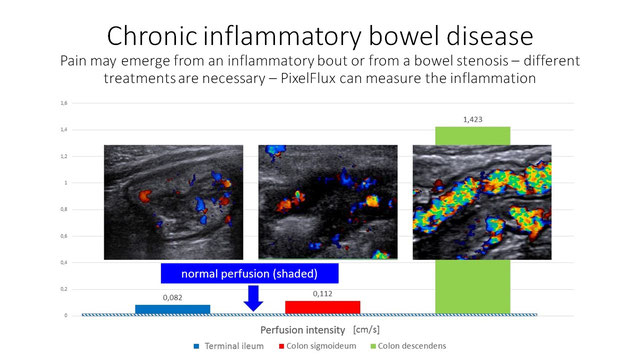
Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like Crohn Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC) often have an intermittend course. During an acute phase of inflammation the intestinal perfusion is increased and pain is stronger. But pain in IBD may also have different sources which must be ruled out. Perfusion measurement of the bowel wall is then a decisive tool.
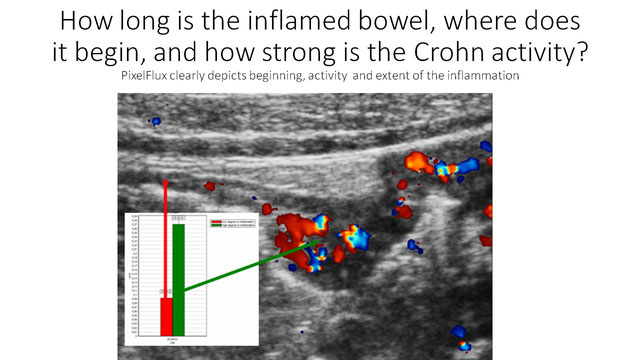
The video below shows acutely inflamed bowel in CD. The thickening of the wall alone cannot decide if the inflammation is active or not since the wall thickening lasts much longer – weeks or months – than the acute hyperperfusion. With PixelFlux measurements of the wall its perfusion can be measured exactly. It is strongly increased. So the diagnosis of an acute exacerbation in CD can be made and – most important for steering the treatment – quantified.
The video below is from a Crohn patient with abdominal pain. PixelFlux-measurements do not show an enhanced perfusion. Thus, no increased inflammatory activity of Crohn disease can be demonstrated. This makes clear that the abdominal pain must be related to another reason than activation of Crohn diesease. To discriminate inflammatory from non-inflammatory causes of pain is crucial for the decision how to treat an individual patient.
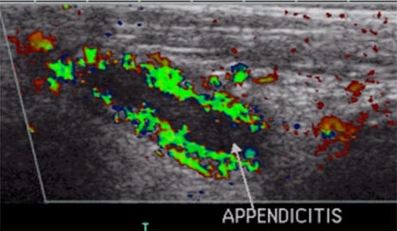
Appendicitis
The inflammation of the vermiform appendix of the cecum can be simply and unambiguously diagnosed by color Doppler sonography. The perfusion measurement with PixelFlux helps much to be sure and to decide, whether operative or conservative treatment is adequate.
Inflammatory renal diseases –
Pyelonephritis, Glomerular Nephritis
Rapid detection of inflammatory bouts in renal diseases are the prerequisite to prevent them from becoming a chronic disorder. PixelFlux-perfusion measurements pinpoint localisation as well as extent of the inflammation. The image below shows a healthy kidney with a normal coloration and a normal perfusion diagram.
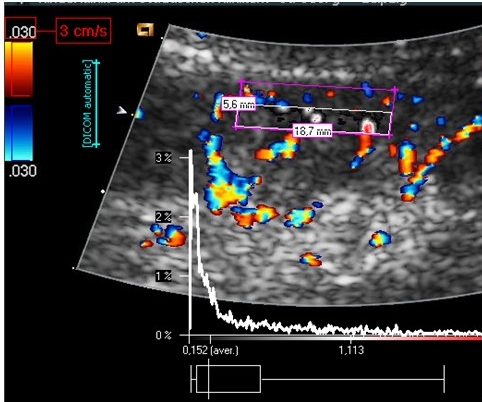
The image below contrasts starkly from the healthy kidney above. Here a massive increase of perfusion unmasks an acute nephritis.